In today’s fast-paced industrial landscape, the need for streamlined and efficient processes is more critical than ever. Companies are constantly seeking ways to optimize their operations, reduce costs, and enhance productivity. This is where the concept of the Automation Pyramid comes into play.
What is the Automation Pyramid?
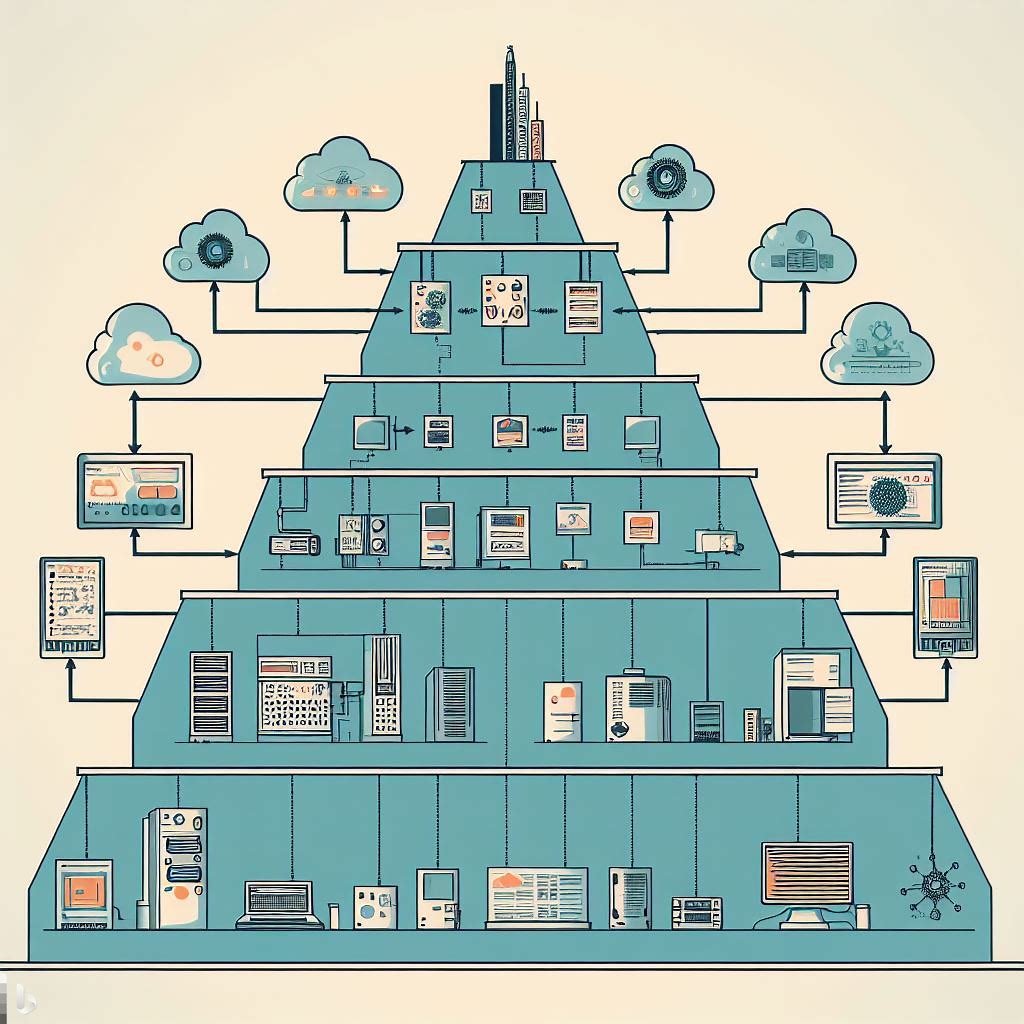
The Automation Pyramid is a model used in the field of industrial automation to illustrate the hierarchical structure of a typical industrial control and automation system. This model is essential for understanding how various components work together to ensure a seamless and efficient operation.
The Automation Pyramid Layers
- Field Level: The base of the pyramid represents the field level. It encompasses sensors and actuators that collect data from the physical environment and interact with it. At the Field Level, various devices, actuators, and sensors are deployed on the production floor, where physical work and monitoring occur. This is where the rubber meets the road, where electric motors, hydraulic and pneumatic actuators move machinery, proximity switches detect material movement, and photoelectric switches identify similar events. These components ensure that the physical aspects of the production process run smoothly.
- Control Level: The Control Level is where decisions are made. Here, PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) and PIDs (Proportional–Integral–Derivative) controllers come into play. PLCs are the brains of the operation, responsible for managing the devices in the Field Level. They gather data from sensors, switches, and input devices, making informed decisions about what outputs to activate to execute predefined tasks. These PLCs consist of processors, memory to store programming and data, and input/output modules.PIDs are often integrated into PLCs and help maintain variables within specified parameters, ensuring precise control of various industrial processes.
- Supervisory Level: Moving up the pyramid, we reach the Supervisory Level, where SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems take the spotlight.SCADA is the bridge that connects lower-level control systems to a centralized supervisory interface. It often includes a Human-Machine Interface (HMI) that enables remote control and monitoring of industrial functions. The beauty of SCADA is its ability to manage and oversee multiple systems from a single location, making it ideal for complex industrial environments.
- Planning Level: The fourth tier of the Automation Pyramid is the Planning Level. At this stage, Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) step in to monitor the entire manufacturing process, from raw materials to the finished product. MES provides management with real-time insights into the manufacturing process, allowing them to make informed decisions. With the data collected from the systems, adjustments to raw material orders and shipment plans can be made swiftly, improving overall efficiency and reducing waste.
- Management Level: At the pinnacle of the pyramid, we find the Management Level. Here, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems reign supreme. ERPs offer top management a comprehensive view and control over all operations within the company. They integrate data from all previous levels, along with additional software, to create a holistic view of the business. This enables efficient monitoring of all aspects, from manufacturing and sales to purchasing, finance, payroll, and more. The integration of ERP promotes transparency and efficiency by aligning every aspect of the business on a single platform.
Automation Pyramid Example
Let’s dive deeper into how the Automation Pyramid works with a real-world example:
Imagine a manufacturing facility producing automobiles. At the Field Level, sensors and actuators monitor the assembly line’s speed, temperature, and other critical variables. These sensors send data to the Control Level, where PLCs manage the manufacturing process, making decisions on actions like painting the car’s body or attaching the wheels.
Operators and supervisors on the Supervisory Level can monitor the entire assembly line using HMIs or SCADA systems. They can detect anomalies, set production parameters, and ensure quality control.
Finally, at the Enterprise Level, decision-makers can analyze the production data, plan for inventory, and schedule maintenance based on the information collected from the lower levels. This enables the company to make informed decisions and enhance overall efficiency.
Industrial Automation Pyramid
Industrial automation is a broad field, and the Automation Pyramid is a fundamental concept within it. The structure remains consistent across various industries, including manufacturing, energy, and utilities.
Implementing an efficient Automation Pyramid can lead to several benefits, such as reduced downtime, improved quality control, and increased production output. It also enables industries to adapt to changes more effectively, ultimately enhancing their competitiveness.
Traditional Automation Pyramid vs. Modern Approaches
While the traditional Automation Pyramid remains a fundamental model, modern industrial automation approaches are evolving. Industry 4.0 and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) are pushing for greater connectivity and integration between the layers. With advanced sensors and data analytics, industries can achieve higher levels of automation and operational efficiency.
In conclusion, the Automation Pyramid is a cornerstone in industrial automation, helping industries create organized, efficient, and effective control and monitoring systems. Whether you’re operating within a traditional pyramid structure or embracing modern automation approaches, understanding this concept is key to success in today’s competitive industrial landscape.
Are you ready to explore the possibilities of automation and boost your efficiency? Consider implementing the Automation Pyramid in your industrial processes, and stay ahead of the curve in the ever-evolving world of automation.
Navigating the Industrial Landscape with Automation Pyramids: A Tale of Two Models
In today’s dynamic industrial landscape, the demand for streamlined and efficient processes has given rise to crucial concepts such as the Automation Pyramid. This model delineates the hierarchical structure of industrial control and automation systems, playing a pivotal role in achieving seamless and efficient operations.
Industrial Automation Pyramid: A Foundation for Structured Management
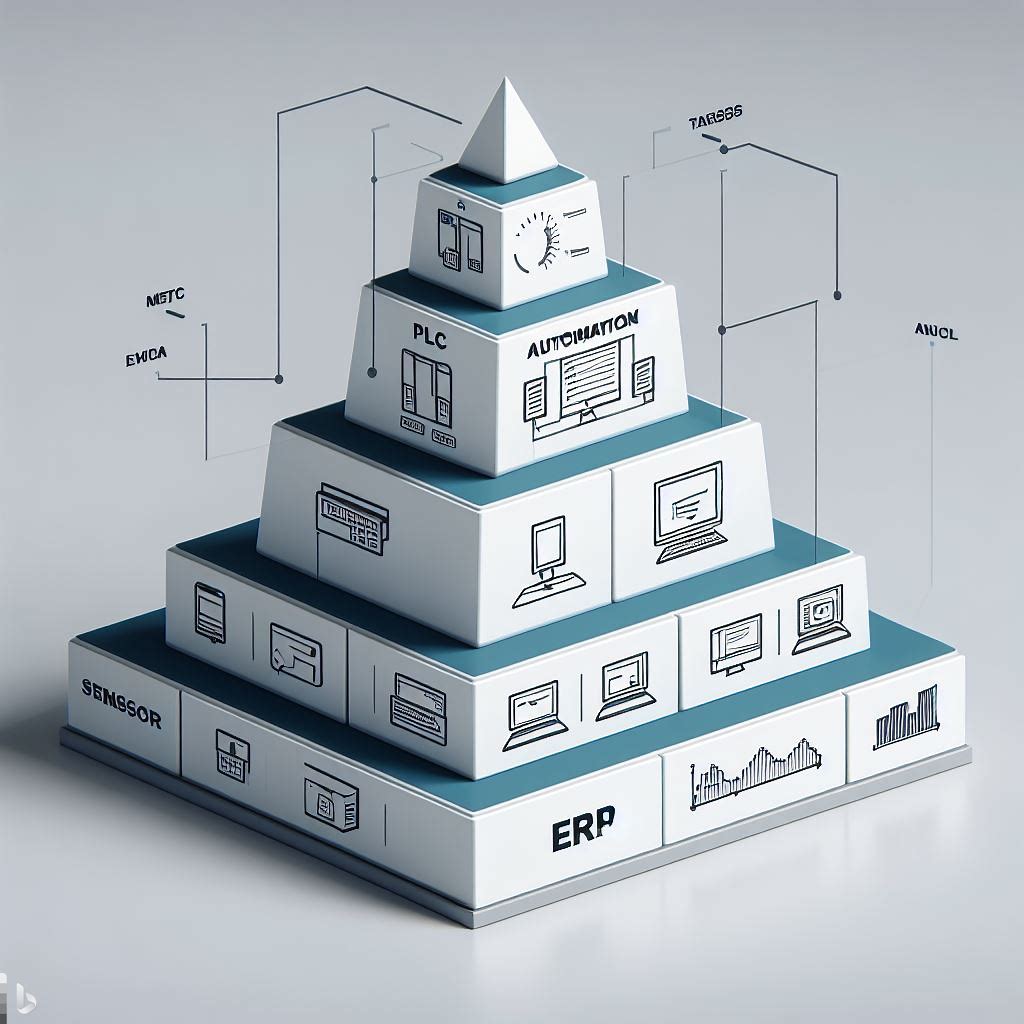
The Industrial Automation Pyramid, as described earlier, encompasses the Field Level, Control Level, Supervisory Level, Planning Level, and Management Level. It provides a structured approach to managing various aspects of industrial processes, from the physical environment to overarching business operations.
Field Level: The foundation of the pyramid, comprising sensors and actuators that interact with the physical environment, gathering and responding to real-time data.
Control Level: The decision-making hub, where PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) and PID (Proportional–Integral–Derivative) controllers manage devices and processes based on sensor inputs.
Supervisory Level: The monitoring and optimization layer, where SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems provide a centralized view of operations, enabling remote control and fine-tuning.
Planning Level: The production optimization stage, where MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) oversee the entire manufacturing process, ensuring efficient resource allocation and adherence to quality standards.
Management Level: The strategic command center, where ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems integrate data from all levels to inform business decisions, resource planning, and supply chain management.
Automation Pyramid of a Smart Factory: Embracing Industry 4.0
The Automation Pyramid of a Smart Factory represents a more advanced and interconnected version of this model. In a Smart Factory, Industry 4.0 and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) drive greater connectivity and integration between the pyramid layers. This results in a more agile and data-driven approach, where real-time insights, predictive analytics, and automation synergize to optimize efficiency and adaptability.
Enhanced Data-Driven Decision Making: Each level of the pyramid collects and analyzes data, providing a comprehensive understanding of the production process and enabling informed decisions.
Unparalleled Connectivity: Seamless communication between all levels fosters real-time data exchange and collaboration, enabling rapid responses to changes and anomalies.
Adaptability and Flexibility: The ability to adapt to changing production demands, new product introductions, and customer requirements ensures long-term sustainability and growth.
A Tale of Two Pyramids: Traditional versus Smart
As industries embrace modern approaches, the distinction between traditional and smart automation becomes apparent. While the traditional Automation Pyramid remains fundamental, providing a structured framework for industrial control, the Smart Factory’s pyramid exemplifies a paradigm shift towards enhanced connectivity, data analytics, and adaptive automation.
Optimizing Your Industrial Processes with Automation Pyramids
Incorporating these concepts into your industrial processes can lead to a myriad of benefits. From reduced downtime and improved quality control to increased production output and greater agility, the Automation Pyramid, whether in its traditional or smart form, equips industries to navigate the complexities of today’s competitive landscape successfully.
Embarking on the Transformational Journey
As you navigate the ever-evolving world of automation, consider the unique advantages each pyramid offers and tailor your approach to meet the specific needs of your industry. Whether aiming for the efficiency of the traditional pyramid or the interconnected brilliance of a Smart Factory, understanding and implementing these concepts are pivotal steps toward staying ahead in industrial automation.
Are you ready to embark on this transformative journey and explore the possibilities that automation holds for your operations? The Automation Pyramid awaits, ready to elevate your industrial processes to new heights.









4 Responses
Excellent information you have shared, thanks for taking the time to share with us such a great article
Thank you for your attention
Please explain about industrial automation pyramid. Regards
Thanks for your attention dear Rik.
We’ll update this blog about automation pyramid of a smart factory soon.